Polylactic Acid (PLA) has emerged as a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics, but many wonder, “Is polylactic acid biodegradable?” This article explores the biodegradability of PLA, examining its chemical composition, degradation conditions, and environmental impact to understand its role in promoting sustainability.
What is Polylactic Acid (PLA)?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a type of bioplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. Known for its eco-friendly properties, PLA is used as an alternative to petroleum-based plastics. It is popular in various applications due to its versatility and relatively low environmental impact.
Common uses of PLA include packaging materials, disposable container and tableware, medical implants, and 3D printing. Its ability to degrade under certain conditions makes it a preferred choice for those looking to reduce plastic pollution and promote sustainability.
(Read more: What is PLA Plastic? Benefits, Uses, and Safety of PLA Material!)
Chemical Composition and Biodegradability of PLA
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a polymer made from lactic acid monomers, which are produced through the fermentation of sugars. The structure of PLA consists of repeating units of lactic acid, forming long chains that give the material its plastic-like properties. PLA can exist in two forms: amorphous and crystalline, each affecting its strength and flexibility.
Key properties affecting the biodegradability of PLA include its molecular weight, crystallinity, and the presence of additives. Higher molecular weight and greater crystallinity generally make PLA more durable but slower to biodegrade. Conversely, additives can either enhance or hinder biodegradability depending on their nature.
Environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, and microbial activity also play crucial roles. PLA typically requires industrial composting conditions—high temperatures and specific microorganisms—to break down efficiently. Under these conditions, PLA can degrade into carbon dioxide, water, and humus within a few months, whereas in natural environments, the process can take significantly longer.
Is Polylactic Acid Biodegradable?
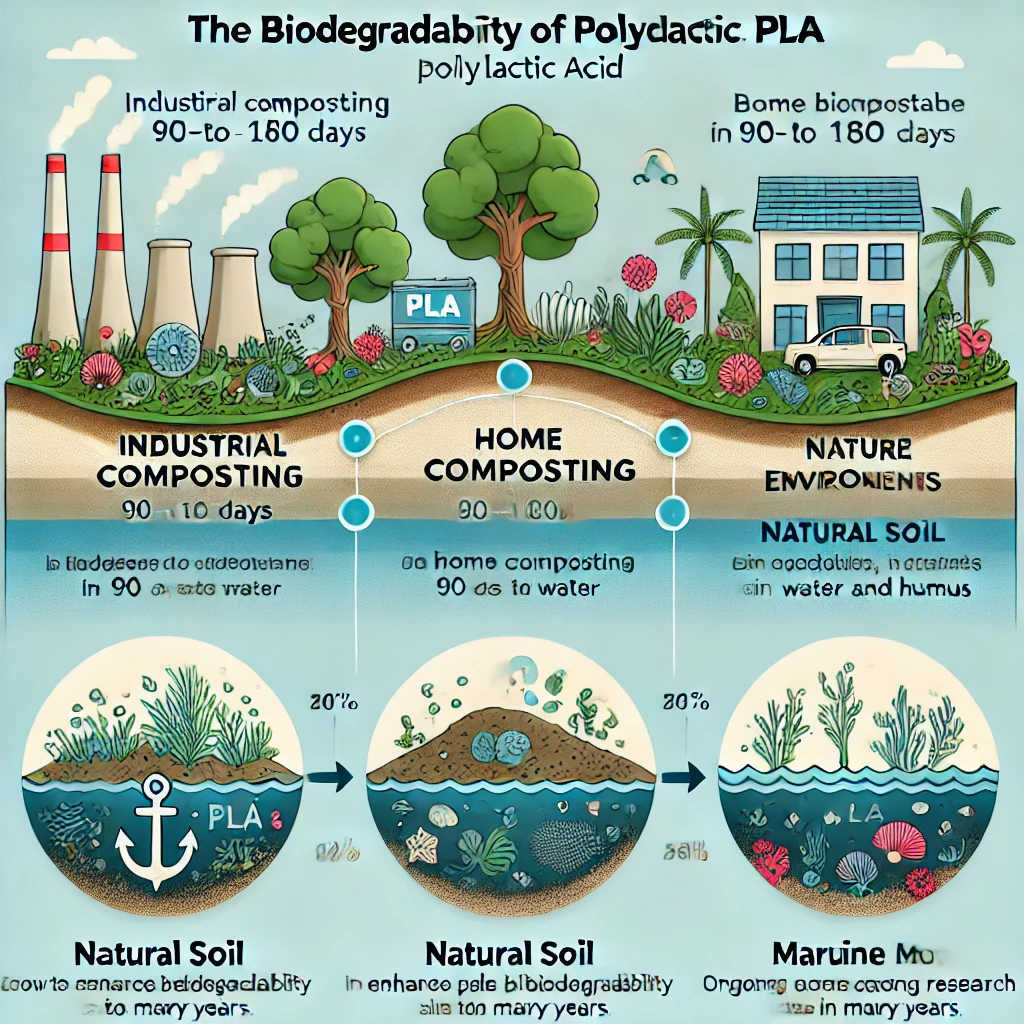
Is polylactic acid biodegradable? The answer is yes, but the rate and efficiency of its degradation depend on the environment. In industrial composting conditions, where temperatures reach 58-60°C and specific microbes are present, PLA can biodegrade within 90 to 180 days, breaking down into carbon dioxide, water, and humus without toxic residues.
In home composting and natural soil conditions, PLA biodegrades much more slowly due to lower temperatures and less optimal microbial activity. It can take several years to decompose in a backyard compost bin and even longer in natural soil, potentially decades, depending on environmental factors such as temperature and moisture levels.
Marine and aquatic environments present the most significant challenge for PLA biodegradation. The cooler temperatures and limited presence of PLA-degrading microbes in water slow down the process considerably. In these settings, PLA can persist for many years, contributing to marine pollution. Ongoing research aims to enhance PLA’s biodegradability in these environments through enzyme treatments and microbial enhancements.
Factors Influencing PLA Biodegradation
The biodegradation of Polylactic Acid (PLA) is influenced by several factors. Is polylactic acid biodegradable? Temperature and microbial activity play crucial roles; higher temperatures and the presence of specific microbes accelerate the breakdown process. Industrial composting conditions provide the optimal environment, while lower temperatures in home composting and natural soil slow down degradation.
PLA blends and additives also affect biodegradability. Blending PLA with other biodegradable materials can enhance its breakdown, while certain additives may either facilitate or hinder the process. The thickness and form of PLA products are additional factors; thinner films and smaller items degrade faster than thicker, more substantial products. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing PLA’s environmental impact and enhancing its biodegradability across different settings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of PLA
The biodegradability of Polylactic Acid (PLA) offers significant environmental benefits, such as reduced reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions. However, is polylactic acid biodegradable in all environments? Challenges remain, including slower degradation in non-industrial settings and potential marine pollution.
Future prospects in PLA technology focus on improving biodegradability through advanced materials and processes, enhancing its sustainability and environmental impact. To explore PLA products and see how they can contribute to a more sustainable future, visit OneNice today.
Recommended articles:
Polylactic Acid Uses and Benefits You Need to Know!
What is PLA Plastic? Benefits, Uses, and Safety of PLA Material!

